How to reduce allergic symptoms in the eyes?
1. What are the manifestations of allergic conjunctivitis?
Spring has arrived, and eye clinics are crowded with a large number of allergic eyes. The typical manifestations of this seasonal allergic conjunctivitis are sudden unbearable eye itching, tearing, redness, severe burning discomfort, conjunctival edema and other discomforts. Symptoms disappear within a few hours after the allergen is removed, and if the allergen is contacted again, the above symptoms reappear immediately. These symptoms are good and bad during the allergic season, recurrent, and related to climate and patient activities. Some patients are also associated with allergic rhinitis, asthma and so on. Allergic conjunctivitis is also characterized by multiple secretions, which are sticky filamentous, different from the purulent secretion of bacterial conjunctivitis, and also different from the watery or serous secretion of viral conjunctivitis.
2. Does allergic conjunctivitis affect vision?
Allergic conjunctivitis generally has no effect on vision, but in order to relieve the symptoms of itching, some patients (especially children) rub their eyes hard, may cause corneal epithelial damage and affect vision, but can be repaired, part of the serious spring khaki In patients with keratoconjunctivitis, the huge nipple formed on the conjunctiva has a damaging effect on the corneal epithelium, and even causes corneal ulcers and seriously affects vision.
3. What is the cause of eye allergies?
When the conjunctiva on the surface of the eye comes into contact with a certain sensitizing substance particle suspended in the air, an allergic reaction may occur, and these allergens are medically referred to as "allergens". When these allergens enter the eye, they bind to the mast cells of the conjunctiva, causing the mast cells to release histamine, causing redness, swelling, and itching. If you get rid of allergens in time, the symptoms can be alleviated or even disappeared. If you continue to contact, other cells in the conjunctiva are involved in the allergic reaction, causing the patient's symptoms to persist or worsen.
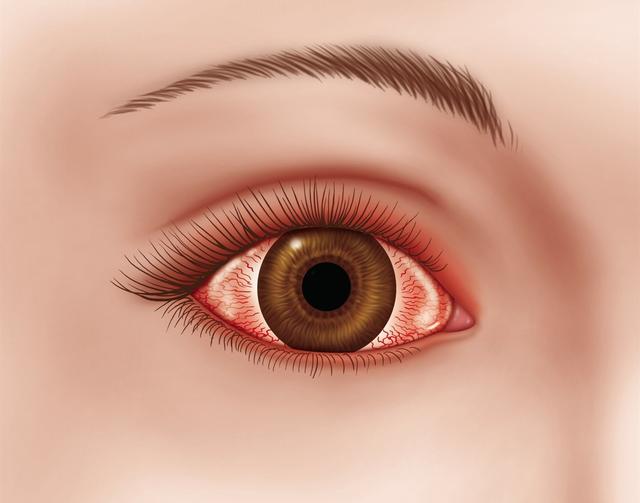
4. How to treat allergic conjunctivitis?
The most important thing for seasonal allergic conjunctivitis is to avoid exposure to allergens immediately and the symptoms can be relieved quickly. If you can't detect or get rid of allergens immediately, you should take medication. The conjunctival sac can be washed with saline to dilute the allergens, alleviating the irritation of the allergens and reducing the symptoms of itching and tearing.
(1) Antihistamines: Antihistamines can only treat mild to moderate allergic conjunctivitis. Severe or frequent patients can be combined with oral antihistamines, but the effect is slower, and the efficacy of allergic conjunctivitis that has already occurred is not good. The use of oral antihistamines may aggravate the symptoms of dry eye patients and further aggravate eye discomfort. Antihistamines should be used with caution in patients with angle-closure glaucoma.
(2) Mast cell stabilizer: mast cell stabilizer local eye can only effectively reduce the degranulation reaction of mast cells in type I hypersensitivity, thus slowing the activation of subsequent eosinophils, neutrophils and monocytes. Gather. However, this process takes 3 to 5 days to achieve the best results, so it is only suitable for the control of the onset of allergic conjunctivitis patients.
(3) antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers double-acting drugs: antihistamines and mast cell stabilizers double-acting drugs are the first choice for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, which can simultaneously stabilize the mast cell membrane and Antagonistic action of histamine, local eye point has a good control effect on the acute inflammatory response and intermittent inflammatory response activation. In addition, clinical studies have confirmed that it can both relieve symptoms and have good tolerance. This class of drugs is recommended for patients with acute phase.
(4) Glucocorticoid drugs: Glucocorticoid drugs can effectively inhibit the activation of various immune cells and the release of inflammatory mediators. It is suitable for patients with severe allergic conjunctivitis and repeated disease progression. The use time should not be too long, should pay attention to follow-up observation, so as not to cause complications such as cataract, glaucoma, fungal infection and delayed healing of corneal epithelium.
(5) Immunosuppressive agents: immunosuppressive agents such as cyclosporine A and tacrolimus local eyedrops have the effect of inhibiting multiple inflammatory mediators and inhibiting conjunctival hypersensitivity mediated by mast cells and T lymphocytes. Inflammatory response. For patients with severe allergic conjunctivitis, especially those who do not tolerate glucocorticoids, ophthalmic preparations of such drugs may be considered. At present, there is still a lack of long-term follow-up data on the safety of such drugs. Therefore, when using such drugs, attention should be paid to observing changes in the patient's condition, and the medication should be adjusted after the disease is relieved.
(6) Other drugs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) local eye can inhibit the production of prostaglandins in type I hypersensitivity, suitable for some mild seasonal allergic conjunctivitis, for acute allergic conjunctivitis limited.
5. How to prevent allergic conjunctivitis?
Trying to avoid or reduce exposure to allergens and improve the living environment can help alleviate and control allergic conjunctivitis. People with pollen allergies need to take protective measures during the pollen season. Dust mites allergic patients should do indoor cleaning and mites work, patients should be properly reduced outdoor activities when air pollution is serious. Secondly, to exercise, enhance physical fitness, regular life and work, pay attention to healthy and appropriate diet, these can make the body's potential to fight allergic attacks, reduce, slow down allergic attacks.
Tips: Patients with allergic conjunctivitis should try to avoid blinking, because the stimulation of blinking can release more allergic factors, make the eyes more itchy, and allergic symptoms worse. For patients with severe symptoms, patients who have not been relieved after many years of treatment may consider changing their living environment, such as moving to another city to live, so that they may be separated from allergens and receive better symptoms of itching, tearing, and foreign body sensation. There is no specificity. Once visual impairment occurs, you should first go to an ophthalmologist for a formal examination and diagnosis.
